Leave Your Message
 Selecting the appropriate pilot-operated diaphragm valve for your specific application is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and reliability in fluid control systems.
According to a recent industry report by MarketsandMarkets, the global diaphragm valve market is projected to grow significantly, with pilot-operated options gaining particular traction due to their efficient sealing capabilities and superior control over flow rates.
With applications spanning across sectors such as water treatment, pharmaceuticals, and food processing, it is essential to consider factors like pressure ratings, material compatibility, and actuation methods.
By understanding these parameters and leveraging data from industry standards, operators can make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements, ultimately enhancing system efficiency and reducing maintenance costs.
Thus, properly assessing the features and specifications of pilot-operated diaphragm valves becomes a fundamental step in optimizing any fluid handling operation.
Selecting the appropriate pilot-operated diaphragm valve for your specific application is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and reliability in fluid control systems.
According to a recent industry report by MarketsandMarkets, the global diaphragm valve market is projected to grow significantly, with pilot-operated options gaining particular traction due to their efficient sealing capabilities and superior control over flow rates.
With applications spanning across sectors such as water treatment, pharmaceuticals, and food processing, it is essential to consider factors like pressure ratings, material compatibility, and actuation methods.
By understanding these parameters and leveraging data from industry standards, operators can make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements, ultimately enhancing system efficiency and reducing maintenance costs.
Thus, properly assessing the features and specifications of pilot-operated diaphragm valves becomes a fundamental step in optimizing any fluid handling operation.
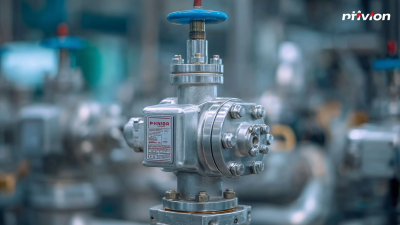
Pilot operated diaphragm valves are essential components in various fluid control applications due to their reliable functionality and ability to regulate flow effectively. Understanding their basic structure and operation is crucial when selecting the right valve for your application. A pilot operated diaphragm valve comprises a diaphragm that opens and closes the valve based on the pilot pressure. This design allows for greater control and responsiveness, making them suitable for industries requiring precise flow management, such as oil and gas or water treatment.
**Tips:** When choosing a pilot operated diaphragm valve, consider factors such as the fluid type, temperature, pressure, and the specific flow characteristics needed for your application. This ensures optimal performance and longevity of the valve. Additionally, it is important to evaluate the compatibility of the valve materials with the fluid to prevent corrosion or degradation over time.
Another key consideration is the valve's size and port configuration. An appropriately sized valve ensures efficient flow rates and minimizes energy loss. Be sure to assess the installation requirements, including space and accessibility for maintenance, to align with the overall design of your system.
When selecting a pilot operated diaphragm valve, understanding key industry standards and specifications is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in various applications. The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) provides guidelines that help maintain safety and efficiency across industries. According to a recent report by the Valve Manufacturers Association (VMA), adherence to ANSI/ISA 75.05 standards can significantly reduce the risk of valve failure, which is a critical aspect when considering the reliability of these valves in process control systems.
Moreover, International Organization for Standardization (ISO) certifications, such as ISO 5208, outline the pressure testing requirements that guarantee valve integrity under varying conditions. Data reveals that valves meeting the ISO standards exhibit a failure rate that is 40% lower than those that do not comply. Understanding the pressure class ratings and leakage classifications as per these standards helps engineers make informed decisions that align with their specific operational needs, whether in water treatment, pharmaceuticals, or chemical processing.
| Specification | Description | Industry Standard | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Valve Size | Determines the flow rate and pipe compatibility. | API 600 | Water treatment, chemical processing |
| Operating Pressure | Maximum pressure the valve can handle. | ASME B16.34 | Oil and gas, HVAC systems |
| Body Material | Material construction affects corrosion resistance. | ASTM A216 | Pharmaceutical, food processing |
| Temperature Rating | The range of temperature the valve can safely operate. | ANSI/ISA 12.27.01 | Power plants, chemical reactors |
| End Connections | Type of connections that determines installation methods. | ISO 7005 | Waterworks, irrigation |
 When selecting a pilot operated diaphragm valve, it is crucial to assess the operating conditions of your application, particularly the pressure, temperature, and flow requirements. Understanding these parameters will guide you in choosing a valve that performs optimally within your system. For instance, if your application involves high-temperature environments, as seen in the recent experimental evaluations of thermal energy storage systems, selecting a diaphragm valve that can withstand elevated temperatures is essential. This ensures that the valve maintains its integrity and functionality under varying thermal loads.
When selecting a pilot operated diaphragm valve, it is crucial to assess the operating conditions of your application, particularly the pressure, temperature, and flow requirements. Understanding these parameters will guide you in choosing a valve that performs optimally within your system. For instance, if your application involves high-temperature environments, as seen in the recent experimental evaluations of thermal energy storage systems, selecting a diaphragm valve that can withstand elevated temperatures is essential. This ensures that the valve maintains its integrity and functionality under varying thermal loads.
Tips:
1. Evaluate the maximum pressure and temperature of your system to ensure the diaphragm valve materials are compatible.
2. Consider the flow requirements; too high of a flow rate could lead to valve wear or failure, whereas too low may result in insufficient performance.
Additionally, innovative measurement techniques, such as those developed for monitoring flow in energy systems, highlight the importance of accurate operational data. By utilizing methods to evaluate flow characteristics, as demonstrated in recent studies on gas distribution in combustion systems, you can fine-tune the selection of your diaphragm valve for better efficiency and reliability in your specific application.
 When selecting a pilot operated diaphragm valve, material considerations are paramount. The choice of diaphragm material can significantly influence the valve's performance and durability in various applications. Common diaphragm materials include elastomers, thermoplastics, and metals, each offering distinct benefits based on the fluid being controlled. For instance, elastomers may provide flexibility and a tight seal, making them suitable for low-pressure applications, while thermoplastics are often chosen for their chemical resistance in more aggressive environments.
When selecting a pilot operated diaphragm valve, material considerations are paramount. The choice of diaphragm material can significantly influence the valve's performance and durability in various applications. Common diaphragm materials include elastomers, thermoplastics, and metals, each offering distinct benefits based on the fluid being controlled. For instance, elastomers may provide flexibility and a tight seal, making them suitable for low-pressure applications, while thermoplastics are often chosen for their chemical resistance in more aggressive environments.
Equally crucial is the composition of the valve body. The material selected for the body must withstand the pressure and temperature conditions it will encounter. Options like stainless steel, cast iron, and various alloys are frequently evaluated based on durability requirements and compatibility with the process media. Assessing both diaphragm and body materials ensures the diaphragm valve not only meets operational demands but also enhances reliability, thereby minimizing maintenance and replacement costs in the long run.
When selecting the appropriate pilot operated diaphragm valve for a specific application, cost-benefit analysis plays a crucial role in understanding long-term performance and maintenance needs. These valves are widely utilized in various industries due to their durability and efficiency. However, evaluating factors such as installation costs, operational efficiency, and potential maintenance needs can significantly influence the decision-making process. Valves that require frequent maintenance could lead to increased operational downtime and higher long-term costs.
Furthermore, just as the aircraft MRO market ensures the safety and efficiency of aircraft through ongoing maintenance and refurbishment, choosing a reliable diaphragm valve involves assessing the performance over time. Implementing a valve that requires minimal maintenance not only enhances operational reliability but also reduces costs associated with repairs and replacements. In this sense, a thorough understanding of the valve's long-term service needs, including the availability of spare parts and technical support, is essential for ensuring optimal performance in demanding applications.